31 Mar The Complete Guide to Phishing Site Takedown
The Complete Guide to Phishing Site Takedown
In a world of ever-changing technology, it’s more important than ever to stay safe online. Unfortunately, that can be difficult when cybercriminals are always coming up with new scams and schemes.
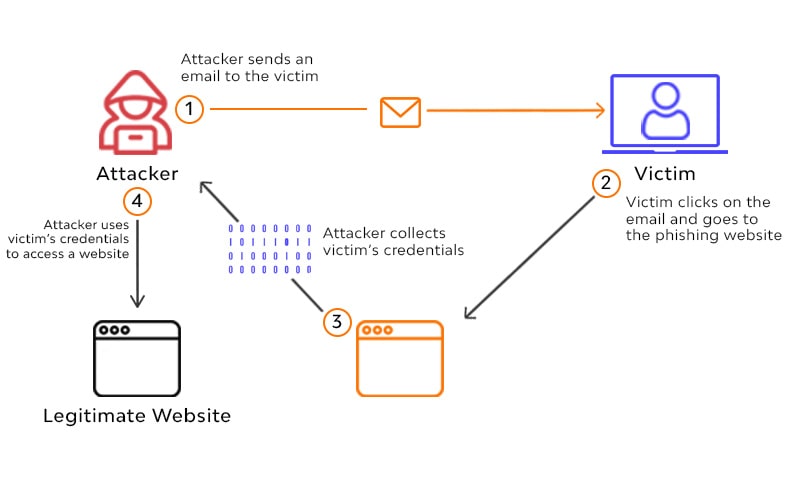
One of the most common tactics is phishing, which involves sending fake emails or creating fraudulent websites to steal personal information.
But thanks to the work of law enforcement and cybersecurity experts, these threats are becoming easier and easier to spot, and we’re taking them down faster than ever before. So if you’re ever unsure about an email or website, don’t hesitate to reach out for help!
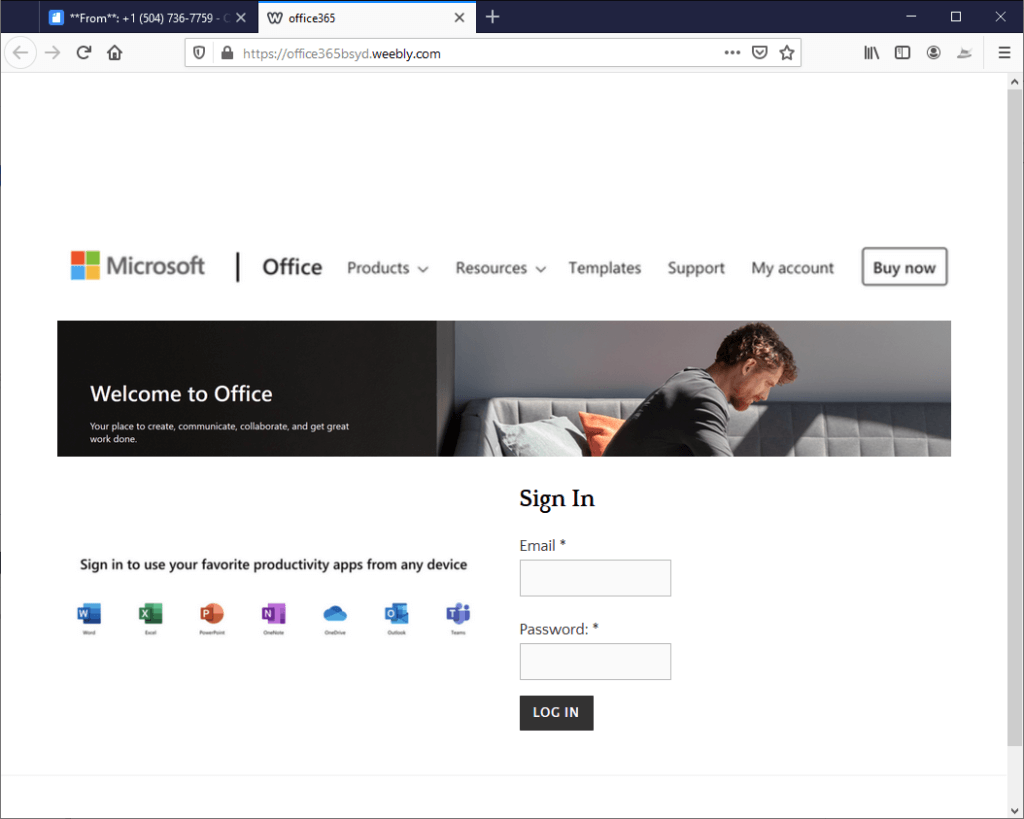
What is a Phishing Site?

A phishing site is a website created to trick someone into entering their personal information, such as login credentials or credit card numbers.
Phishing sites often look very similar to legitimate websites but with slight differences in the web address or the site’s design.
Phishing emails typically contain links to these fake websites and sometimes ask the recipient to enter sensitive information.
Be very careful when clicking on links in emails, especially if the email claims to be from a trusted source.
If you’re not sure whether a website is legitimate, you can always do a quick Google search for reviews or the official website address.
Impact of Phishing Attacks on a Business
Phishing attacks can have a significant impact on a business. They can result in the theft of sensitive information, such as credit card numbers or login credentials, which can be used to commit fraud or identity theft.
Phishing attacks can also damage a company’s reputation and cause financial losses. In addition, they can be costly to remediate, which can disrupt business operations and adversely affect the bottom line.
Businesses should protect themselves from phishing attacks by deploying anti-spam and antivirus software, training employees to recognise phishing emails, and establishing policies and procedures for responding to security incidents.
Loss of Intellectual Property
Phishing attacks can result in the loss of confidential information, such as product specifications or proprietary software code. Hackers may use this information to create counterfeit products that compete with the company’s legitimate products.
To protect against this, companies should restrict access to sensitive files and assign each unique employee credentials for accessing them. They should also limit unauthorised access through firewalls and control who can download data from servers.
Business Disruption
A phishing attack usually causes an immediate disruption. Still, it can also lead to unexpected downtime or business disruptions in the future if hackers decide to exploit their initial entry into your systems for criminal gain at a later date.
For example, they could leave backdoors on your network to allow them to regain access to your systems for malicious purposes quickly.
You can prevent this by updating all passwords and software immediately after being notified that there’s been a security breach and by keeping an eye out for suspicious activity on your network and servers.
Damage to Reputation
Phishing attacks can damage a business’s reputation if hackers successfully fool customers or other users into disclosing personal information or making fraudulent transactions through the phishing site.
For example, they could send emails claiming that an eCommerce company is having problems with their services but directing users to visit a spoofed website where they’re prompted to enter credit card details to keep their account active or check order statuses.
To prevent this, companies should inform customers via email and other channels to alert them that there may be a phishing attack underway and provide instructions on how to spot the spoofed site.
Loss of Money
A company can suffer financial loss due to a phishing attack if its internet-facing systems are compromised. Hackers use their access for fraudulent purposes, such as initiating wire transfers or making online purchases, which cause monetary losses for the business.
To prevent this from happening, companies should ensure that all eCommerce sites and interfaces with third parties (e.g., payment processors) are secure by regularly updating passwords and tightening access controls.
They should also watch for any unusual transactions in their accounting system indicating suspicious activity.
Steps on Taking Down Phishing Sites
The following steps are the general order for a phishing site takedown:
1. Gather information about the site and its owner. This will include IP addresses, domain name registration details, etc.
2. Research if the site is a phishing website or a false positive report. False positives occur when a legitimate website gets flagged as malicious by an antivirus program or other security tool hacked into, falsely flagging it as dangerous. If there is doubt over whether you have found a phishing website, verify this information with Anti Fraud Companies.
They can also send you the necessary papers for hosting companies to remove content from their network under copyright infringement claims.
3. Notify the hosting company that the site violates its terms of service or copyright infringement laws. You can find information about contacting them by doing a Whois search.
Remember that phishing sites are illicit, so be extremely careful what information you share with companies. Sometimes they will keep your contact information for their records even if you ask them not to do so.
4. If there’s no response after 2-3 weeks, then legal complaints should be sent through fax and email (not first-class mail) using the DMCA (Digital Millennium Copyright Act).
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) is a US copyright law that provides guidelines for online service provider liability in copyright infringement. You should take this step only if you have exhausted all other efforts to get the site taken down and know who the site’s hosting company is.
However, there is an effortless way for you to take down a phishing website. With a professional phishing site takedown software, you can be assured that a malicious website will be taken down as soon as it gets spotted.
The time here is essential for you as a business owner because the criminals might affect your brand’s reputation with indecent attempts.
Conclusion
The takedown process can be complicated and frustrating, especially if a hosting company does not take your requests seriously or provide timely responses to your phone calls and emails.
However, don’t give up! If one site is taken down successfully, another will pop up unless we work together as a community to stop these phishing sites from being created in the first place. It is crucial to understand how phishing sites are made to do this.
The post The Complete Guide to Phishing Site Takedown is by Stuart and appeared first on Inkbot Design.


